UL risk management is implemented in accordance with the UL Quality Policy and is one of the elements of quality management system. The UL Risk Management System provides for risk management in the core processes of the UL, as well as in long-term projects, including integrated assessment of financial management, corruption and work safety.
The UL manages the following groups of risks in its core business processes:
- Study processes;
- Scientific and research processes;
- IT proceses and Data Security.
The UL provides risk management for the following groups of long-term projects:
- Academic Centre Development Programme projects;
- Study Development and Governance Enhancement Programme projects.
The management of other UL processes and project groups risks is integrated within the framework of the risk management of these processes. Risks are assessed at both strategic and operational levels.
The aims of the UL risk management are:
- to identify the negative or positive consequences of the potential events in their qualitative and quantitative expression, which can potentially affect the attainment of the UL goals, and to respond in a timely manner to avoid or minimise harm or maximise benefits;
- to reduce inefficient or irrational use of resources and potential future losses from adverse events, and to identify opportunities for the improvement of UL operations and development;
- identify and define process risks, plan their management.
Risk management principles at the UL:
- precautionary principle and avoiding excessive risk;
- an integrated approach to managing corruption risks, occupational safety risks, IT security risks and personal data protection risks;
- the principle of ensuring the continuity of the management process, as well as timely control.
Risk management is one of the elements of internal control system (ICS). ICS at UL is a continuous cycle of control environment, risk assessment, implementation of control measures, information and communication, as well as monitoring (COSO model).
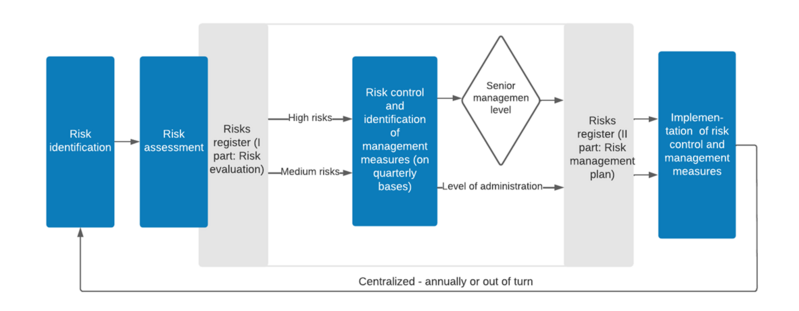
UL staff are involved in the identification of risks, while process owners and staff responsible for the risk areas to be managed in an integrated way (Independent Risk Management Committee) are involved in the assessment of risks and the definition of medium-level risk control and management measures. High-level risks are managed at the level of the UL governance (see Figure).
The UL risk tolerance is dominated by the precautionary principle and the principle of avoiding excessive risk, therefore the objectives of the Risk Management implemented by the UL are mainly related to the prevention of adverse events and the identification of opportunities for improvement of UL performance.
UL employees are responsible for identifying risks and implementing planned management measures in their field of activity, including the following responsibilities:
- to understand and implement risk management processes in executing their daily responsibilities;
- to report to the supervisor all risks, including inefficient, ineffective or ineffectual controls, incidents or accidents;
- to cooperate in analysing the causes of risks;
- to reduce or eliminate risks within the scope of their job responsibilities.
Risk owner is responsible for risk management in the owned process or project by:
- providing the necessary measures for identifying process or project risks;
- getting in assessing the risks of a process or project, analysing their causes and identifying risk management measures;
- ensuring the implementation of the risk management measures;
- performing risk monitoring and getting involved in their regular update.
Quality Manager is responsible for ensuring the successful implementation and continued operation of the risk management system by:
- developing, implementing, validating and regularly reviewing the risk management system and its documentation, and ensuring its maintenance, monitoring and improvement in cooperation with Risk owners and the Standing Risk Management Committee;
- organising the process of risk identification, assessment and determination of risk management measures, and ensuring the establishment and maintenance of risk registers;
- recording data on identified risks, as well as the planned and implemented measures for risk mitigation;
- ensuring that the risk management measures identified in UL risk registers are incorporated into the UL Task Management System, and monitoring their implementation;
- compiling and submitting risk management reports to the UL governance.
Composition of Standing Risk Management Committee:
- Chair of the UL Quality Advisory Committee;
- UL Chancellor;
- UL Internal Auditor;
- Head of the UL Occupational Safety Management System
- UL employee responsible for corruption risk management;
- UL employee responsible for personal data security;
- UL Data security manager.
Standing Risk Management Committee:
- provides integrated risk management of the UL working environment, IT security, corruption, financial and process risks by engaging in risk assessment and root cause analysis of the UL processes and projects;
- advises risk owners and the quality manager on the choice of risk management measures.
UL management
- determines the risk management policy and risk management structure;
- identifies the significant risks and their owners;
- decides on measures and actions to prevent or mitigate high-level risks.
UL Council:
- monitor the functioning of internal control and risk management systems, review their adequacy and operational effectiveness

 CONFERENCE
CONFERENCE